Table Of Content
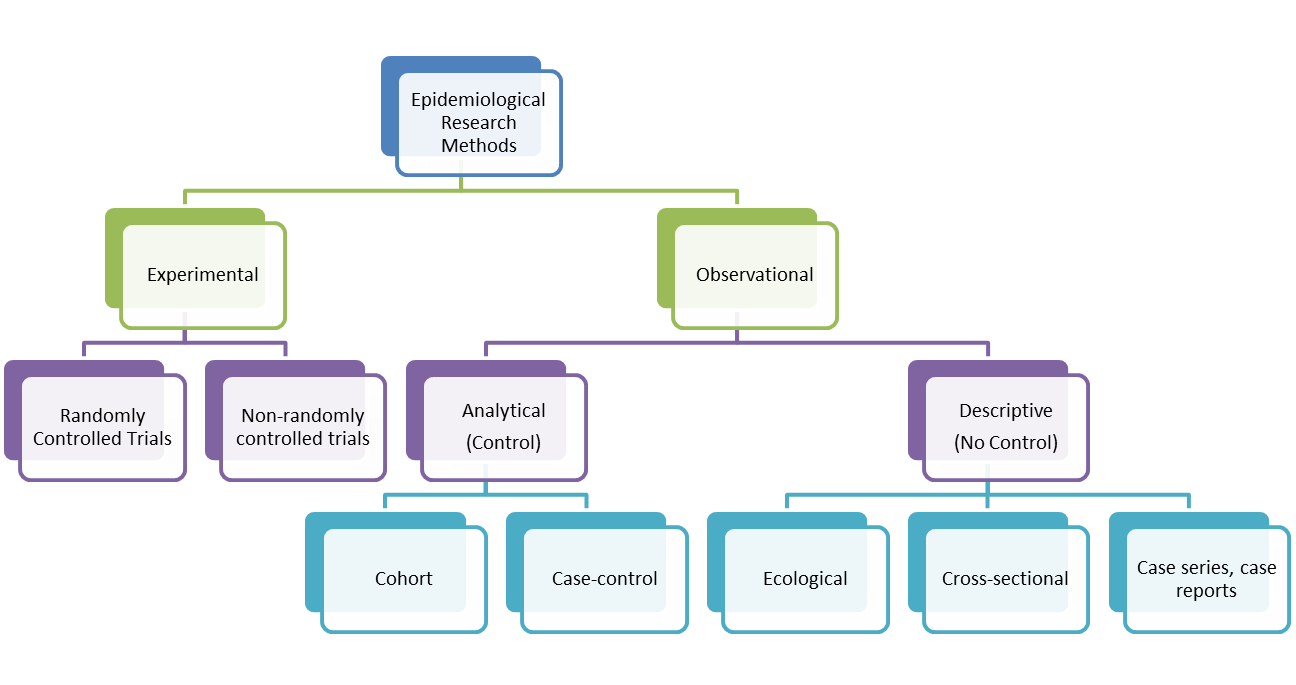
In cross-sectional studies, the validity of results is highly dependent on whether the study sample is well representative of the population proposed to be studied, and whether all the individual measurements were made using an accurate and identical tool, or not. If the information on a variable cannot be obtained accurately, for instance in a study where the participants are asked about socially unacceptable (e.g., promiscuity) or illegal (e.g., substance use) behavior, the results are unlikely to be reliable. If these data are analyzed only to determine the distribution of one or more variables, these are “descriptive.” However, often, in a cross-sectional study, the investigator also assesses the relationship between the presence of an exposure and that of an outcome. Such cross-sectional studies are referred to as “analytical” and will be discussed in the next article in this series. The main purpose of descriptive research design is to describe and measure the characteristics of a population or phenomenon in a systematic and objective manner. It involves collecting data that describe the current status or condition of the population or phenomenon of interest, without manipulating or altering any variables.
Documentary survey
Simon et al. (2015) used a qualitative descriptive design to identify the perspectives of seriously ill, older patients and their families on the barriers and facilitators to advance care planning. The authors provided a rationale for using a descriptive design, which was to gain a deeper understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. Data were gathered through nine open-ended questions on a researcher-administered questionnaire. Three categories were developed that identified personal beliefs, access to doctors and interaction with doctors as the central barriers and facilitators to advance care planning. The use of a qualitative descriptive design facilitated the development of a schematic based on these three themes, which provides a framework for use by clinicians to guide improvement in advance care planning. As previously identified, a further challenge with the use of qualitative descriptive methods is that as a research design it has limited visibility in research texts and methodological papers (Kim et al., 2017).
UI/UX Designer Job Description for 2024 - Simplilearn
UI/UX Designer Job Description for 2024.
Posted: Wed, 03 Apr 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Observational Research – Methods and Guide
Choosing the appropriate research design for a study is crucial to the success of the study. Moreover, researchers should choose a design that best fits the research question and the type of data needed to answer it. Descriptive research often requires a large amount of data collection and analysis, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. The primary purpose of descriptive research is to describe the characteristics, behaviors, and attributes of a particular population or phenomenon. The research will provide a more accurate picture of a population’s demographic makeup and help to understand changes over time in areas like population age, health and education level.
Descriptive research allows for cross sectional study

Similarly, lacking encouragement in professional development, nurses are unable to cultivate pride or confidence, or envision their future. Sandelowski (2010) argues that although descriptive research produces findings that are ‘data-near’, they are nevertheless interpretative. Although it is important to ensure those familiar with the topic under investigation can recognise their experiences in the description of it (Kim et al., 2017), this is not to say that there should be no transformation of data. Researchers using a qualitative descriptive design need to, through data analysis, move from un-interpreted participant quotations to interpreted research findings, which can still remain ‘data-near’ (Sandeklwoski, 2010). Willis et al. (2016) suggest that researchers using the qualitative descriptive method might report a comprehensive thematic summary as findings, which moves beyond individual participant reports by developing an interpretation of a common theme.
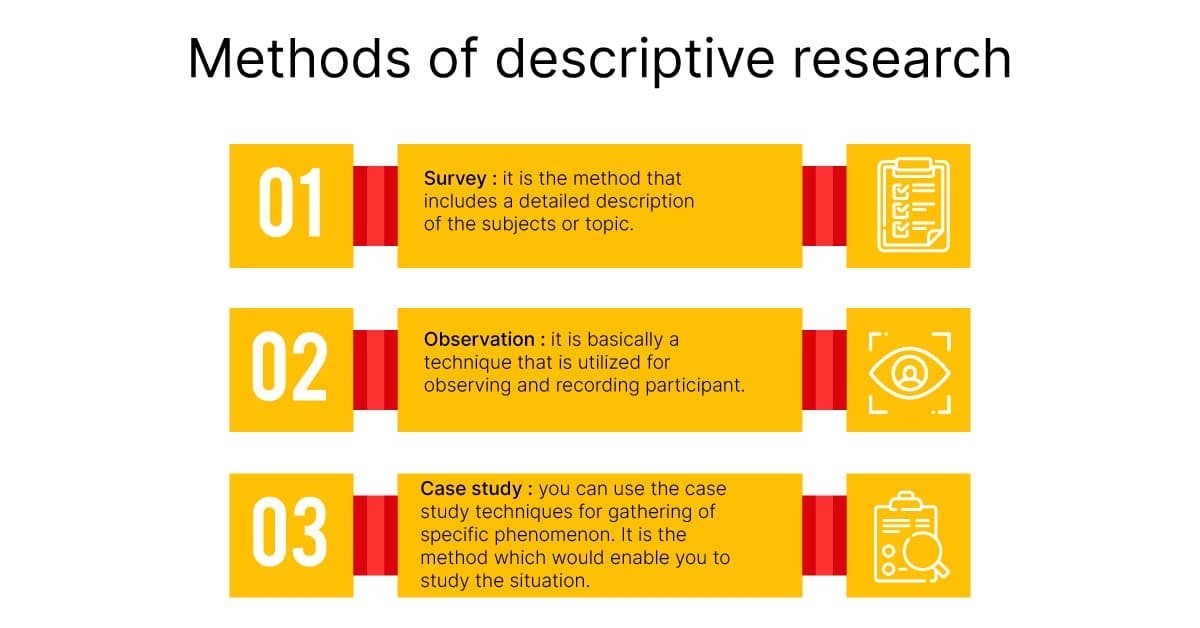
Use observational methods
Descriptive research focuses on providing a detailed and accurate account of a specific situation, group, or phenomenon. It aims to describe the characteristics, behaviors, or relationships within the given context. Descriptive research typically involves collecting data through surveys, observations, or existing records and analyzing the data to generate descriptive statistics or narratives.
Aims
Descriptive research design is widely employed across diverse fields, and its primary objective is to systematically observe and document all variables and conditions influencing the phenomenon. Give your users any and all relevant information so that they can truly experience the photo. Therefore, the aim of this study is to explore the factors that facilitate the retention of nurses who have returned to work, from their perspectives. Some words that design professionals may use to describe their work include uplifting, grand, bright, sleek, and so on. Leverage survey analytics software that allows you to run statistical analysis and observe data on a live dashboard. Once you’ve clearly stated your criteria and objectives, you must also specify the nature of the data that must be gathered.
Writing a good review article
A unit's experience with hybrid NICU design: description of care model and implications for patients, families, and ... - Nature.com
A unit's experience with hybrid NICU design: description of care model and implications for patients, families, and ....
Posted: Tue, 12 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
This means that novice qualitative researchers have little guidance on how to design and implement a descriptive study as there is a lack of a ‘methodological rulebook’ to guide researchers (Kahlke, 2014). Despite the widespread use of descriptive approaches within nursing research, there is limited methodological guidance about this type of design in research texts or papers. This suggests there is a need to have more discussion about how and why descriptive approaches to qualitative research are used.
Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses
This design is particularly useful when the differences in exposure between individuals within a group are much smaller than the differences in exposure between groups. For instance, the intake of particular food items is likely to vary less between people in a particular group but can vary widely across groups, for example, people living in different countries. A descriptive study is one that is designed to describe the distribution of one or more variables, without regard to any causal or other hypothesis.
Numerous policies have been implemented on a global scale to address the persistent shortage of nursing professionals. These policy measures encompass creating new registered nurses through education; facilitating re-entry into the nursing workforce for currently inactive registered nurses, and recruiting nurses from other countries [4]. Among the aforementioned strategies, one particularly promising approach to overcoming the nursing shortage involves the recruitment of inactive nurses, which has been implemented in many countries [4, 5]. The reintegration of inactive nurses into the labor force is advantageous in terms of cost and time, as it obviates the need to invest social capital and years of resources in educating and nurturing new nursing students.
A cross-sectional study is a type of observational study that involves gathering information on various variables at the individual level at a given point in time. Annemarie Brady (PhD, MSc, BNS, RNT, RPN) is Chair of Nursing and Chronic Illness and Head of School of Nursing and Midwifery at Trinity College Dublin. Her research work has focused on the development of healthcare systems and workforce solutions to respond to increased chronic illness demands within healthcare. This paper provides an overview of qualitative descriptive research, orientates to the underlying philosophical perspectives and key characteristics that define this approach and identifies the implications for healthcare practice and policy. A descriptive study design’s statistical capabilities allow researchers to track data trends over time.
Instead, it focuses on providing a detailed and accurate representation of the data collected, which can be useful for generating hypotheses, exploring trends, and identifying patterns in the data. Because of the exploratory nature of descriptive design, the triangulation of multiple sources of data are often used for additional insight into the phenomenon. Sources of data that can be used in descriptive studies are similar to those that may be used in other qualitative designs and include interviews, focus groups, documents, artifacts, and observations. Arguments supporting the flexible nature of descriptive designs describe it as being preferable to forcing a research approach into a design that is not quite appropriate for the nature of the intended study. However, descriptive design has also been criticized for this mixing of methods as well as for the limited literature describing it.
No comments:
Post a Comment